Understanding Baseball Field Chart Positions
Baseball, often dubbed “America’s pastime,” captivates millions with its strategic gameplay and unpredictable moments. At the heart of this beloved sport lies the baseball field, a meticulously designed arena where every position plays a crucial role. Whether you’re a newcomer eager to grasp the basics or a seasoned fan brushing up on your knowledge, understanding Baseball Field Chart Positions is key to appreciating the intricacies of the game.
Decoding the Baseball Diamond: A Position-by-Position Guide
A standard baseball field comprises several key areas: the infield, the outfield, and the pitcher’s mound. Each of these areas is home to specific player positions, each with unique responsibilities. Let’s delve into the roles and characteristics of each position:
The Infield: The Heart of the Action
-
Pitcher (P): Positioned on the pitcher’s mound, the pitcher’s primary role is to deliver the ball to the catcher, aiming to prevent the batter from hitting it. Pitchers are known for their diverse throwing styles, from fastballs that blaze past batters to curveballs that dance across the plate.
-
Catcher (C): Crouched behind home plate, the catcher is the field general, calling pitches and receiving the ball. They are responsible for catching foul balls, preventing stolen bases, and communicating with the pitcher throughout the game.
-
First Baseman (1B): Holding down first base, the first baseman’s primary responsibility is to catch throws from other infielders to make outs. They also play a crucial role in fielding ground balls hit towards first base.
-
Second Baseman (2B): Positioned between first and second base, the second baseman covers a lot of ground, fielding ground balls, tagging runners, and covering second base on steal attempts.
-
Third Baseman (3B): Known as the “hot corner” due to hard-hit balls coming their way, the third baseman requires quick reflexes and a strong arm. They field ground balls, catch line drives, and cover third base on steal attempts.
-
Shortstop (SS): Occupying the area between second and third base, the shortstop is often considered the captain of the infield. Their responsibilities include fielding ground balls, throwing to first base for outs, and covering second base on steals.
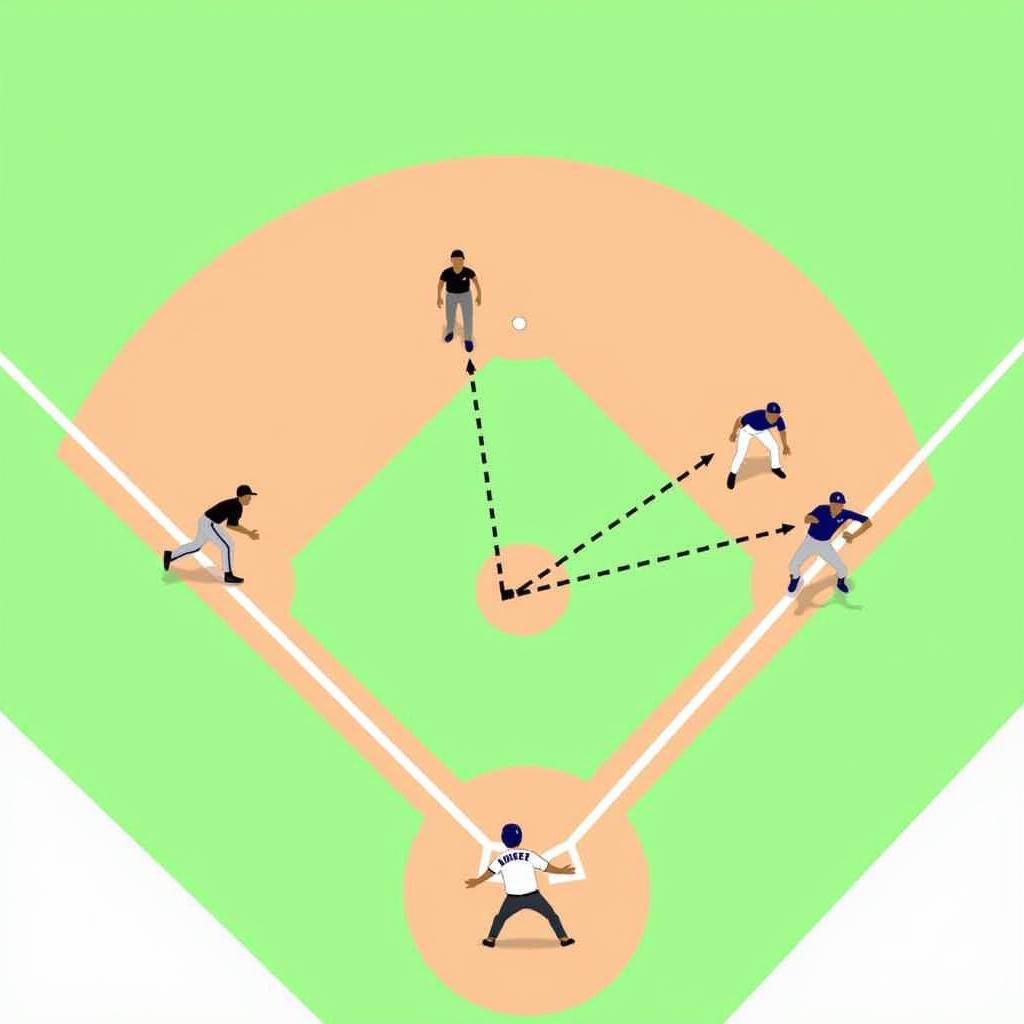 Baseball Infield Positions
Baseball Infield Positions
The Outfield: Patrolling the Open Grass
-
Left Fielder (LF): Covering the left portion of the outfield, the left fielder tracks down fly balls, throws to the appropriate base to prevent runners from advancing, and backs up the infield on ground balls.
-
Center Fielder (CF): Patrolling the vast center field, the center fielder possesses exceptional speed and range. They are responsible for catching deep fly balls, directing other outfielders, and backing up plays in both left and right field.
-
Right Fielder (RF): Holding down right field, the right fielder mirrors the left fielder’s responsibilities on the opposite side of the field. They catch fly balls, make throws to prevent runs, and back up the infield on ground balls.
 Strategic Outfield Alignment in Baseball
Strategic Outfield Alignment in Baseball
Beyond the Basics: Strategic Depth and Lineup Variations
Understanding the basic baseball field position template is just the beginning. Baseball teams often employ strategic variations based on the game situation, pitcher’s strengths, and batter’s tendencies.
-
Defensive Shifts: Teams may shift their infielders to different positions based on the batter’s likelihood to hit the ball to a particular side of the field.
-
Depth charts mlb: Teams have a roster of players who can fill different positions, providing flexibility and strategic options throughout the game.
-
MLB Baseball Lineup: The order in which players bat is strategically determined based on their hitting abilities, speed, and ability to get on base.
Baseball Field Chart Positions: The Foundation of the Game
Mastering the fundamentals of baseball field chart positions opens the door to a deeper appreciation for the sport’s strategic depth. Each position requires a unique skillset, athleticism, and understanding of the game. Whether you’re analyzing defensive alignments, admiring a spectacular catch in center field, or celebrating a perfectly executed double play, knowing where players are and what they do enhances your enjoyment of this timeless game.
FAQs About Baseball Field Positions
1. What is the most challenging position in baseball?
While all positions demand skill, the catcher’s role is often considered the most physically and mentally demanding. They are involved in every pitch, require protective gear, and must make split-second decisions.
2. Which position is known for its offensive power?
Historically, corner infielders (first base and third base) and outfielders tend to be power hitters, often occupying the heart of the batting order.
3. Do players ever switch positions during a game?
Yes, players can switch positions during a game for strategic reasons, such as late-inning defensive replacements or if a player gets injured.
4. How does the field’s dimensions impact gameplay?
Field dimensions vary, with some parks favoring hitters (shorter fences) and others favoring pitchers (larger outfields). These variations influence offensive and defensive strategies.
5. What resources can I use to learn more about baseball positions?
Numerous websites, books, and videos provide detailed information about baseball positions, including player profiles, historical data, and coaching tips.
Need More Information on Baseball?
For a deeper dive into the world of baseball, including insights into top salaries mlb, player statistics, and historical records, explore the wealth of resources available online and at your local library.
Contact us:
For any assistance please contact Phone Number: 0989060241, Email: [email protected] Or visit us: Hamlet 2, Commune 5, An Phuong, Hon Quan, Binh Phuoc, Vietnam. Our customer service team is available 24/7.

